Introduction to Programming - (C Language) - Unit : 2 - Iterative Statements / Looping Statements
ITERATIVE STATEMENTS/LOOPING STATEMENTS
The loops in C language are used to execute a block
of code or a part of the program several times.
In other words, it
iterates a code or group of code many times.
Why use loops in C language?
Suppose that you have to
print table of 2, then you need to write 10 lines of code.
By using the loop
statement, you can do it by 2 or 3 lines of code only.
Advantage of loops in C
1) It saves code.
2) It helps to traverse
the elements of array (which is covered in next pages).
Types of C Loops
There are three types of
loops in C language that is given below:
- do
while
- while
- for
while loop in C
The while loop in C language is used to iterate the part of program or statements many times.
In while loop, condition
is given before the statement. So it is different from the do while loop. It
can execute the statements 0 or more times.
When use while loop in C
The C language while loop should be used if number of iteration is uncertain or unknown.
Syntax of while loop in C language
The syntax of while loop
in c language is given below:
while(condition)
{
//code to be executed
}
Flowchart of while loop in C
Example of while loop in C language
Let's see the simple
program of while loop that prints table of 1.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <conio.h>
void main()
{
int i=1;
clrscr();
while(i<=10)
{
printf("%d \t",i);
i++;
}
getch();
}
Output
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Program to print table for
the given number using while loop in C
#include <stdio.h>
#include <conio.h>
void main()
{
int i=1,number=0;
clrscr();
printf("Enter a number: ");
scanf("%d",&number);
while(i<=10)
{
printf("%d \n",(number*i));
i++;
}
getch();
}
Output
Enter a number: 5050100150200250300350400450500Enter a number: 1001002003004005006007008009001000
Infinitive while loop in C
If you pass 1 as a
expression in while loop, it will run infinite number of times.
while(1)
{
//statement
}
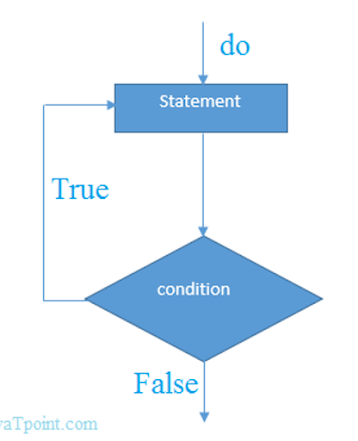
do while loop in C
To execute a part of
program or code several times, we can use do-while
loop of C language. The code given between the do and while block will be
executed until condition is true.
In do while loop,
statement is given before the condition, so statement or code will be executed at lease one time. In other words, we can say it is executed 1 or more times.
It is better if you have
to execute the code at least once.
do while loop syntax
The syntax of C language
do-while loop is given below:
do
{
//code to be executed
}while(condition);
Flowchart of do while loop
do while example
There is given the simple
program of c language do while loop where we are printing the table of 1.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <conio.h>
void main()
{
int i=1;
clrscr();
do
{
printf("%d \t",i);
i++;
}while(i<=10);
getch();
}
Output
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Program to print table for the given number using do while loop
#include <stdio.h>
#include <conio.h>
void main()
{
int i=1,number=0;
clrscr();
printf("Enter a number: ");
scanf("%d",&number);
do
{
printf("%d \n",(number*i));
i++;
}while(i<=10);
getch();
}
Output
Enter a number: 55101520253035404550Enter a number: 10102030405060708090100
Infinitive do while loop
If you pass 1 as a
expression in do while loop, it will run infinite number of times.
do
{
//statement
}while(1);
For Loop in C
When you need to execute a block of code several number of
times then you need to use looping concept in C language. In C Programming
Language for loop is a statement which allows code to be
repeatedly executed. It contains 3 parts.
·
Initialization
·
Condition
·
Increment or
Decrements
Syntax
for ( initialization; condition; increment ){ statement(s);}· Initialization: This step is execute first and this is execute only once when we are entering into the loop first time. This step is allow to declare and initialize any loop control variables.
·
Condition: This is next step after initialization step, if it is true, the
body of the loop is executed, if it is false then the body of the loop does not
execute and flow of control goes outside of the for loop.
·
Increment or Decrements: After completion of Initialization and Condition steps loop body
code is executed and then Increment or Decrements steps is execute. This
statement allows to update any loop control variables.
Note: In
for loop everything is optional but mandatory to place 2 semicolons (; ;)
Example
for() // Error
for( ; ; ) // valid
Flow Diagram
Control flow of for loop
· First initialize the variable, It execute only once when we are entering into the loop first time.
·
In second
step check condition
·
In third step
control goes inside loop body and execute.
·
At last
increase the value of variable
·
Same process
is repeat until condition not false.
Example of for loop
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
int i;
clrscr();
for(i=1;i<5;i++)
{
printf("\n%d",i);
}
getch();
}
Output
1234Important Points
·
In for loop
if condition part is not given then it will repeats infinite times, because
condition part will replace it non-zero. So it is always true like.
for( ; 1; )
·
For loop is
repeats in anti lock wise direction.
·
In for loop
also rechecking process will be occurred that is before execution of the
statement block, condition part will evaluated.
Example
while(0) // no repetition
for( ; 0; ) // it will repeats 1 time







Comments
Post a Comment